- Room No.- 02, Department of ENT & HNS. Dhaka Medical College Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- 01672755508
- Login
03
Feb
2025
- 194
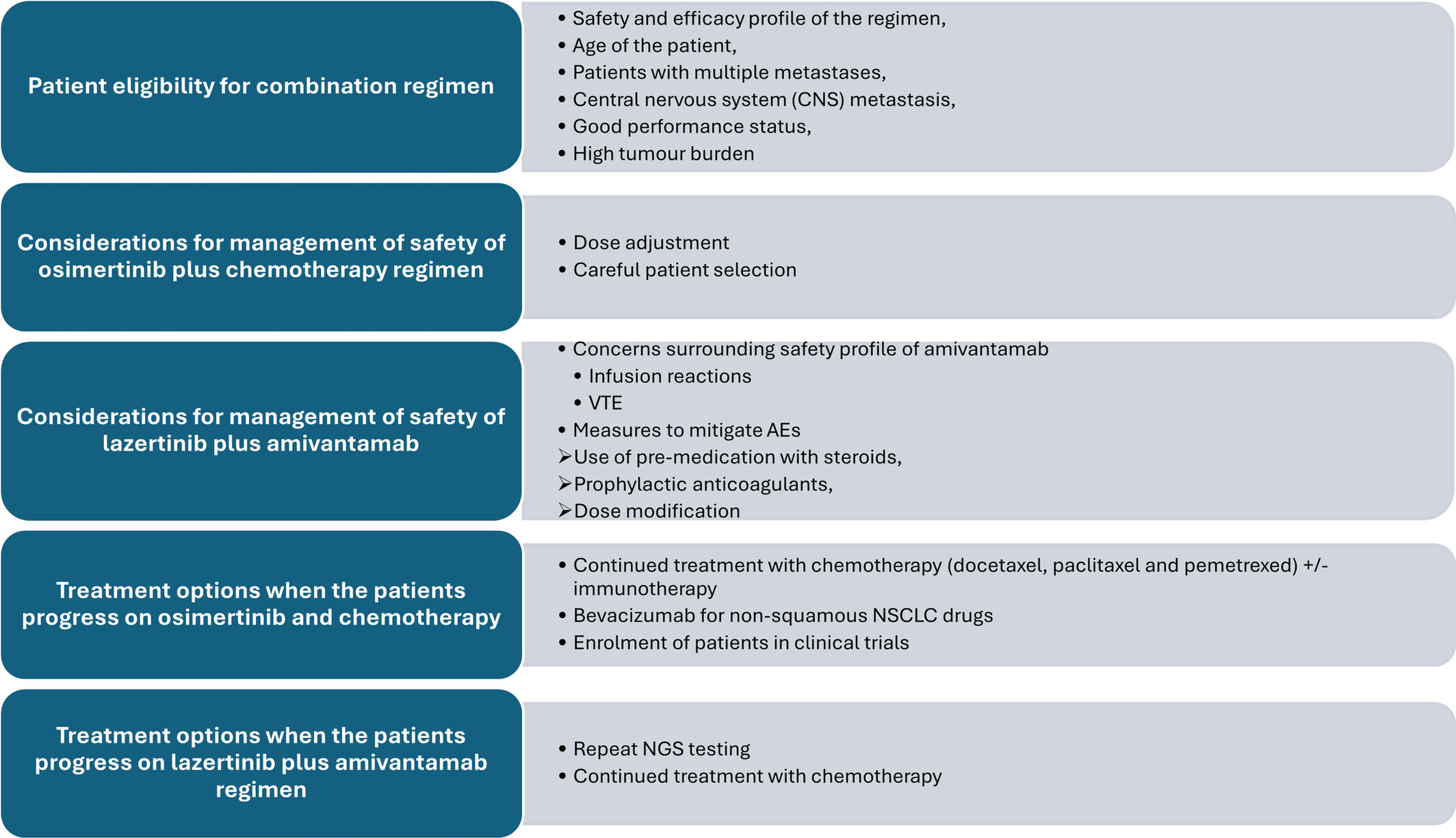
Management of stage IV EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer in Asia.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) testing is recommended to be included in the reimbursement scheme, and the turnaround time of testing should be shortened, considering the high burden of the disease in Asia. The panel recommended careful selection of patients for osimertinib+chemotherapy or lazertinib+amivantamab based on safety and efficacy profile, patient age, and disease status. While the panel agreed that osimertinib+chemotherapy is acceptable for these patients, dose adjustment and careful patient selection are recommended to optimize safety outcomes. For lazertinib+amivantamab, measures to mitigate adverse events such as the use of pre-medication with steroids, prophylactic anticoagulants, and dose modification are recommended. For patients progressing on one of the combination regimens, experts recommended repeat NGS testing and continued treatment with chemotherapy.
What's New?
Emerging strategies for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) featuring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are helping improve patient outcomes. Which strategies are optimal to effectively manage EGFR-mutant NSCLC, however, remains unclear. This study gathered insight on the diagnosis and treatment of advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC from a panel of lung cancer experts in Asia, where the lung cancer burden is high. Notably, the panel recommended next-generation sequencing for identifying patients for EGFR TKI treatment and favored osimertinib plus chemotherapy over lazertinib plus amivantamab. The findings cast light on current diagnostic and treatment patterns for advanced EGFRm NSCLC.
Lung cancer experts from Asia recommend NGS for the appropriate selection of patients for EGFR TKI treatment. The experts emphasize selecting patients with specific clinical profiles for the combination regimen to balance the risk–benefit ratio. Most participants favored the osimertinib plus chemotherapy regimen over lazertinib plus amivantamab due to its familiarity with AE management, cost, and availability in the Asia region. Additionally, recommendations were made regarding the management of safety profiles for both regimens and the management of NSCLC patients post-progression on osimertinib.






